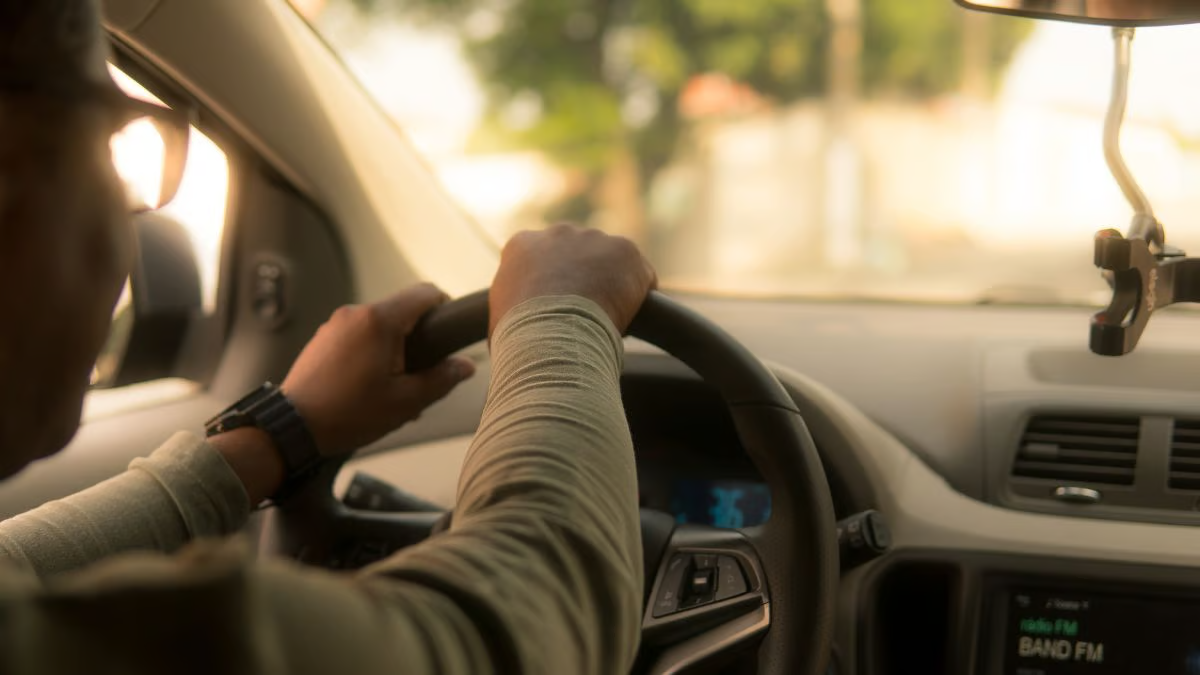
New Delhi: A recent status report submitted to the National Green Tribunal (NGT) by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has revealed that some flame-retardant chemicals found in car cabin air, which may be carcinogenic, are not listed under the Manufacture, Storage, and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules 1989. This report highlights a potential regulatory gap, as these rules were issued by the Union Ministry of Environment.
The CPCB’s report, dated September 10, 2024, noted that no testing had been conducted on these chemicals and recommended that the tribunal consult agencies overseeing automobile safety standards, which are regulated by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
This issue gained attention in June when the NGT’s principal bench, led by Justice Prakash Shrivastava, took suo motu notice of a media report indicating the presence of “carcinogenic flame retardants” in cars. The claim, which is being investigated by the US National Toxicology Program, prompted the NGT to request a report from CPCB on the matter.
According to CPCB, the media report detailed a study that analysed the cabin air of 101 cars—electric, gas, and hybrid models from 2015 to 2022. The research found that 99% of these vehicles contained a flame retardant known as TCIPP. The study also identified two additional flame retardants, TDCIPP and TCEP, which are considered carcinogenic and linked to neurological and reproductive issues.
The report further suggested that the source of these harmful chemicals is the seat foam, which manufacturers use to meet outdated flammability standards that may not offer real fire-safety benefits. The flame retardants TCIPP, TDCIPP, and TCEP are not included in the MSIHC Rules 1989, according to CPCB.
CPCB explained that while the Union Ministry of Environment has established effluent and emission standards for various chemical industries, including those producing plasticisers and aromatics, automobile safety standards are set by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways. These standards are enforced by the Automotive Research Association of India and the National Automotive Testing and R&D Infrastructure Project. However, CPCB has not conducted specific studies on these flame retardants used in automotive products.